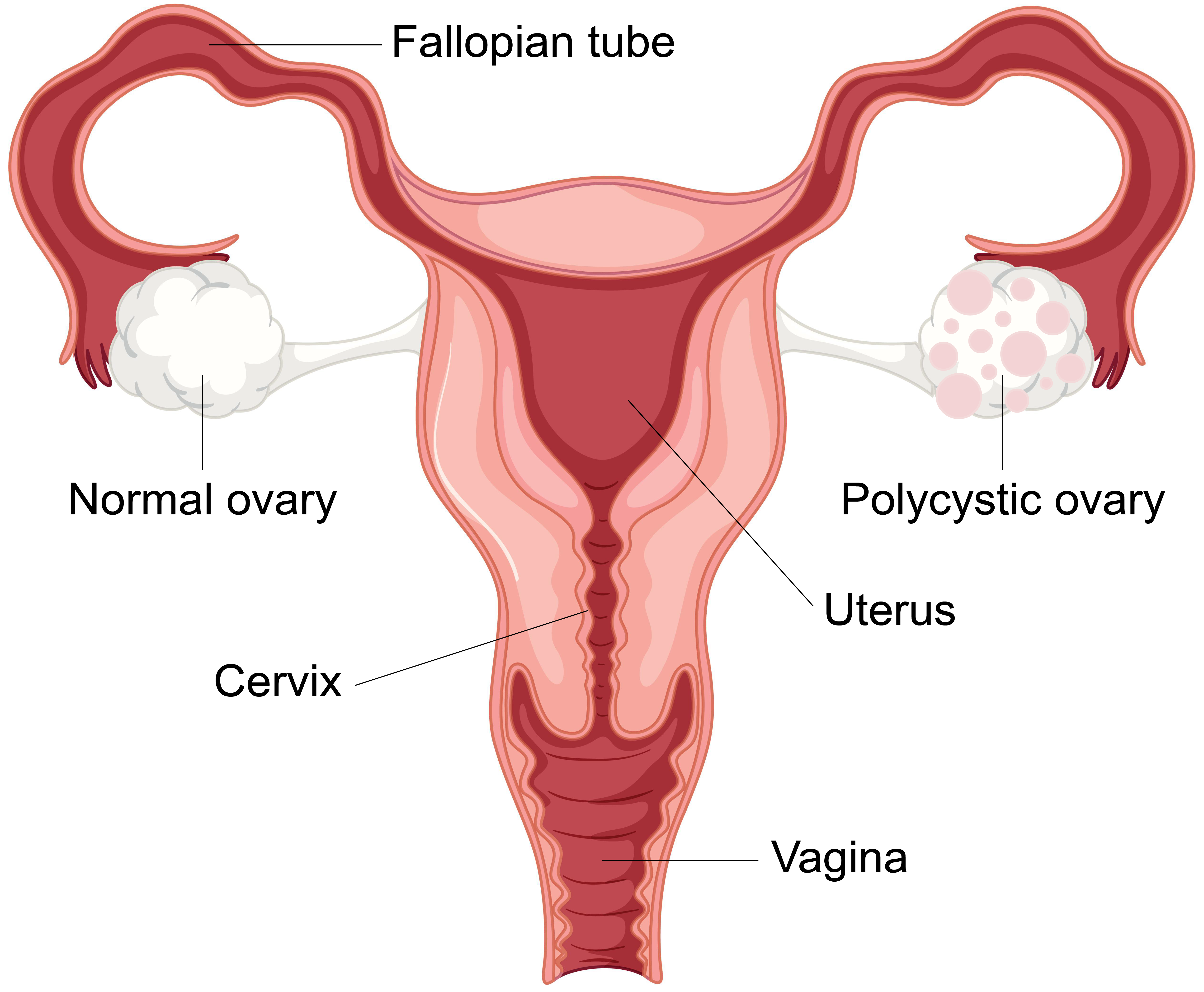
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It can cause a range of symptoms, from irregular periods to difficulty conceiving, and can lead to long-term health problems if left untreated. In this blog post, we’ll explore what PCOS is, its symptoms, causes, how it’s diagnosed, and the various treatment options available to manage this condition.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
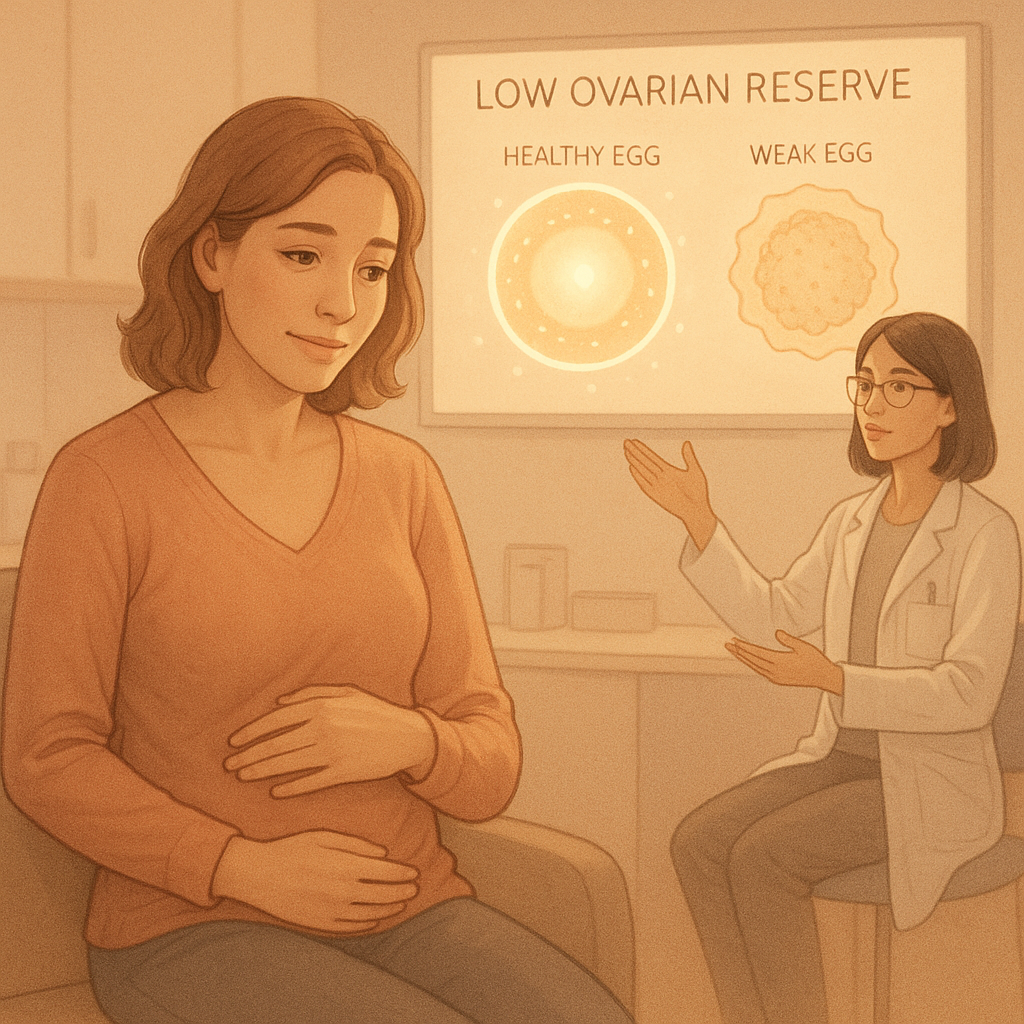
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition where a woman’s ovaries become enlarged and develop multiple small cysts. These cysts are actually immature follicles that have failed to release eggs. This causes hormonal imbalance polycystic ovary syndrome that can affect a woman’s menstrual cycle, fertility, and overall health. While polycystic ovary syndrome is not a life-threatening condition, it can impact a woman’s quality of life, making it important to understand how to manage it.
PCOS is one of the most common causes of infertility in women, but with proper treatment and lifestyle management, women can improve their chances of conceiving and reduce the symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
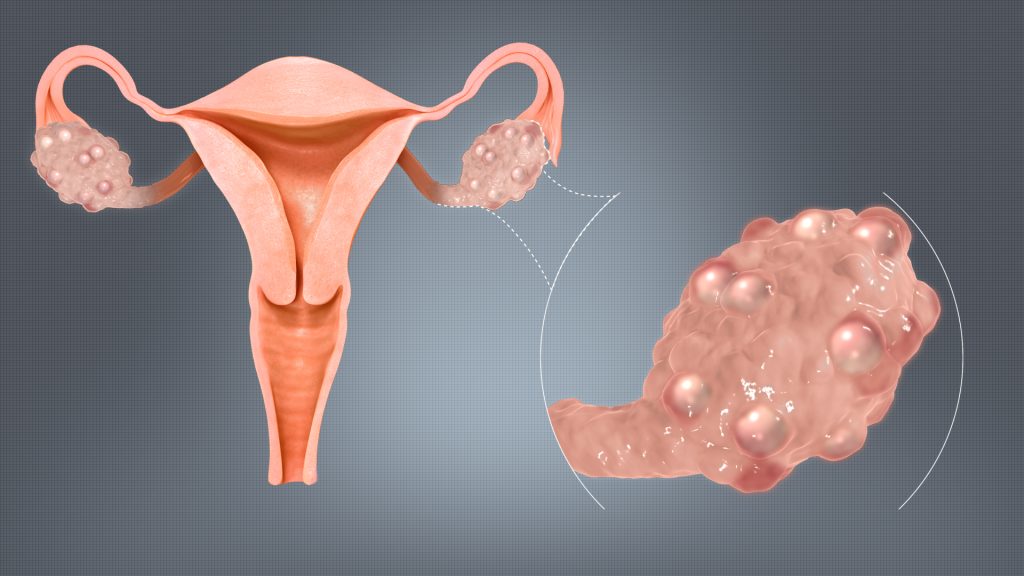
What Are the Common Symptoms of PCOS?
- Irregular Periods: Women with PCOS often have irregular or missed periods. This can be one of the first signs of the condition.
- Excess Hair Growth (Hirsutism): Many women with PCOS develop excessive hair growth on their face, chest, or abdomen due to elevated androgen levels.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Increased androgens (male hormones) can lead to acne, particularly on the face, chest, and back.
- Thinning Hair: Women with PCOS may experience thinning of the hair on the scalp, a condition known as male-pattern baldness.
- Weight Gain or Difficulty Losing Weight: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight gain, especially around the abdomen, and find it difficult to lose weight.
- Is there polycystic ovary syndrome causes infertility?: Polycystic ovary syndrome infertility is a common problem, as the hormonal imbalance prevents ovulation, making it harder for women to get pregnant.
In addition to these symptoms, women with PCOS may also experience fatigue, depression, and mood swings due to hormonal imbalances.
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
To diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome pcos, healthcare providers usually perform a combination of tests and evaluations, including:
- Physical Examination: The doctor may check for signs such as excessive hair growth, acne, or scalp thinning.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound may be used to examine the ovaries and check for the presence of cysts.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure hormone levels, including testosterone, insulin, and others related to the menstrual cycle.
- Medical History: The doctor will review the patient’s menstrual history, weight, and other polycystic ovary syndrome symptoms to help make a diagnosis.
PCOS is diagnosed when a woman meets at least two of the following criteria:
- Irregular or absent periods.
- High levels of male hormones (androgens), leading to symptoms like excess hair growth or acne.
- Multiple cysts on the ovaries as seen on an ultrasound.
Causes and Risk Factors of PCOS
The exact causes of polycystic ovary syndrome are not fully understood, but there are several factors that are believed to contribute to its development.
What Causes Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
-
- Hormonal Imbalance: One of the main causes of PCOS is an imbalance in the reproductive hormones, particularly an excess of androgens (male hormones like testosterone). This hormonal imbalance affects the ovaries, preventing them from releasing eggs regularly.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which means their bodies do not use insulin efficiently. As a result, the body produces more insulin, which can lead to weight gain and worsen symptoms.
- Genetics: PCOS tends to run in families, so if a woman’s mother or sister has the condition, she is more likely to develop it herself.
How Does Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Occur?
Polycystic ovary syndrome occurs when the ovaries do not release eggs regularly due to hormonal imbalances. The ovaries develop multiple cysts as a result, and the hormonal disruption also leads to problems with ovulation. The excess insulin produced in the body worsens the hormonal imbalances and may also affect a woman’s ability to conceive.
Can You Prevent PCOS?
Currently, polycystic ovary syndrome cannot be prevented, as its causes are largely genetic and hormonal. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Does PCOS Cause Infertility?
Yes, PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility. The hormonal imbalance in women with PCOS prevents ovulation, making it difficult for them to conceive. However, with proper treatment and management, many women with PCOS are able to get pregnant.
Treatment Options for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
While there is no cure for PCOS, there are several polycystic ovary syndrome treatments that can help manage symptoms and treatment improve quality of life. Treatment plans will vary depending on a woman’s symptoms, age, and whether she is trying to conceive.
Medical Treatments for PCOS
- Birth Control Pills: Oral contraceptives are often prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce excess hair growth, and clear up acne by balancing hormone levels.
- Metformin: This medication is commonly used to treat insulin resistance, a common issue in women with PCOS. It helps lower blood sugar levels and can help with weight management and ovulation.
- Fertility Medications: If a woman with PCOS is trying to conceive, doctors may prescribe medications like Clomid or Letrozole to induce ovulation. In more severe cases, injectable hormones or IVF (in vitro fertilization) may be recommended.
Nutritional Therapies for PCOS
A healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing polycystic ovary syndrome. Eating a balanced diet that stabilizes blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss can help manage symptoms. Recommended dietary strategies include:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods that do not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar can help with insulin resistance.
- Increased Fiber: Fiber-rich foods like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can help with weight management and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Herbal Treatments for PCOS
Some women with PCOS turn to herbal treatments as part of their management plan. Common herbs used to regulate menstrual cycles and balance hormones include:
- Vitex (Chaste Tree Berry): Known for its ability to regulate the menstrual cycle and balance progesterone levels.
- Saw Palmetto: May help reduce excess hair growth caused by elevated testosterone levels.
- Spearmint Tea: Drinking spearmint tea may help lower androgen levels and reduce hirsutism (excess hair growth).
It is essential to discuss herbal treatments with a healthcare provider before starting, as some herbs may interact with other medications.
How to Manage Polycystic Ovary Syndrome with Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle changes can help women with PCOS manage their symptoms more effectively:
- Regular Exercise: Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, help with weight management, and regulate hormone levels.
- Healthy Eating: A balanced, nutrient-rich diet is essential for managing PCOS and preventing complications like diabetes and heart disease.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, so practicing stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be helpful.
Can Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Go Away?
While PCOS is a lifelong condition, its symptoms can be managed effectively with treatment and lifestyle changes. The hormonal imbalances and other issues associated with PCOS may persist, but many women find that their symptoms can be significantly reduced, especially with medical intervention and healthy lifestyle adjustments.
Living with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Living with PCOS can be challenging, but with the right support and treatment plan, women can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Understanding the condition and its symptoms is key to managing it effectively. Regular visits to a healthcare provider, including specialists like those at the Cyprus IVF Clinic, can help women with PCOS get the care they need to manage the condition and achieve their reproductive goals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
What is PCOS, and how does it affect women’s health?
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects a woman’s ovaries, leading to irregular periods, excess hair growth, and difficulty conceiving. It can also increase the risk of long-term health issues like diabetes and heart disease.
How is PCOS diagnosed by healthcare professionals?
PCOS is diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and ultrasounds to check for cysts in the ovaries and hormonal imbalances.
What are the best treatment options for managing PCOS symptoms?
The best treatment for PCOS depends on the individual’s symptoms and whether they are trying to conceive. Common treatments include birth control pills, fertility medications, insulin-sensitizing drugs, and lifestyle changes.
Is it possible for PCOS symptoms to go away with lifestyle changes or medical treatment?
While PCOS cannot be cured, many women find that their symptoms improve significantly with the right combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and nutritional therapy. Regular monitoring and care can help women live well with PCOS.