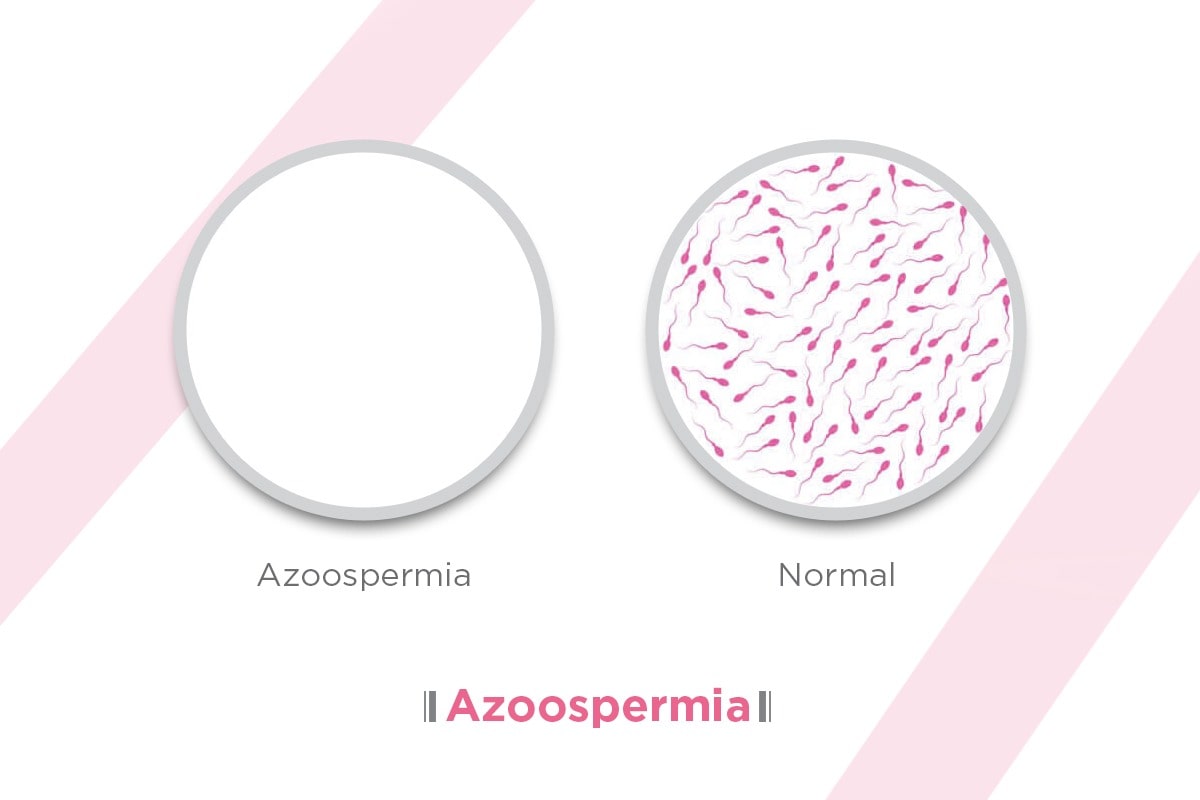
Azoospermia is a medical term used to define the complete absence of sperm in a man’s ejaculate. This condition affects approximately 1% of the male population and is one of the leading causes of male infertility. When couples are unable to conceive naturally, male fertility testing often reveals this condition as a potential factor. Understanding the basics of what is azoospermia is the first step in identifying the right medical support and treatment pathways.
While azoospermia may seem like a discouraging diagnosis, the rapid advancements in reproductive medicine have made it possible for many affected individuals to father children. Through early diagnosis, personalized evaluation, and targeted intervention, the condition can often be managed or treated effectively. In the following sections, we will explore the azoospermia meaning, common symptoms, underlying causes, and treatment options, including assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF.
What is Azoospermia?
Azoospermia is defined as the total absence of sperm cells in a man’s semen during ejaculation. It is a medical condition that affects about 10-15% of infertile men and is a major cause of male infertility. The diagnosis is typically made through a semen analysis, where a laboratory examination shows no detectable sperm under a microscope. It is important to note that azoospermia does not always mean there is no sperm production at all; in some cases, sperm may be produced but blocked from being released.
To better understand the condition, we must look at how experts define azoospermia. The term comes from the Greek words “azoos” (without life) and “sperma” (seed), indicating semen without living sperm. Azoospermia can result from genetic, hormonal, structural, or environmental factors. It is classified into two main types: obstructive azoospermia, where there is a physical blockage, and non-obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is severely impaired or absent. Correct identification of the type is essential for choosing the most effective treatment approach.
What Causes Azoospermia?
The causes of azoospermia can be complex and vary significantly from person to person. Generally, azoospermia is divided into two main categories: obstructive and non-obstructive. Obstructive azoospermia occurs when sperm production is normal but a physical blockage prevents sperm from reaching the ejaculate. Common causes include vasectomy, congenital absence of the vas deferens (often associated with cystic fibrosis), infections, or past surgeries. Non-obstructive azoospermia, on the other hand, results from impaired or absent sperm production in the testicles due to hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, or damage from chemotherapy or radiation.
Understanding azoospermia causes is essential for selecting the correct treatment path. Hormonal deficiencies, especially low levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or luteinizing hormone (LH), may disrupt the sperm production process. In some cases, testicular failure can occur due to trauma, undescended testicles, or varicocele. Genetic abnormalities such as Klinefelter syndrome and Y-chromosome microdeletions are also well-documented reasons for azoospermia. Identifying the root cause through a combination of blood tests, imaging, and genetic analysis is critical for successful fertility treatment.
What are the Symptoms of Azoospermia?
One of the most challenging aspects of diagnosing azoospermia is that it typically presents no obvious physical signs or symptoms. Most men with this condition are unaware of any issue until they attempt to conceive with their partner and face difficulties. Since the body still produces semen fluid without sperm, the ejaculate often appears normal, making the condition invisible without laboratory testing. As a result, azoospermia symptoms are usually only discovered during a fertility evaluation or routine semen analysis.
That said, some symptoms may be indirectly linked to the underlying causes of azoospermia. For example, men with hormonal imbalances may experience reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, or abnormal breast growth (gynecomastia). Those with obstructive causes might have a history of testicular surgery, infection, or trauma. In rare cases, small or soft testicles may be a sign of low sperm production. It is crucial to undergo a full fertility workup to determine whether the absence of sperm is due to an obstruction or a production issue.
How is Azoospermia Detected?
Azoospermia is usually first detected during a routine semen analysis, where the sample is examined under a microscope. If no sperm is observed, the test may be repeated to confirm the result. Advanced detection methods, such as centrifugation of the semen sample or specialized staining techniques, may help reveal rare sperm that are not initially visible.
How is Azoospermia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing azoospermia involves more than just semen analysis. Once no sperm is detected, doctors typically conduct hormone tests to assess testosterone, FSH, and LH levels. Genetic testing may also be performed to identify chromosomal abnormalities. In certain cases, a testicular biopsy is required to determine whether sperm production is occurring within the testes, helping guide further treatment options.
How Does Azoospermia Affect Pregnancy?
The presence of azoospermia significantly impacts a couple’s ability to conceive naturally. Since there are no sperm cells in the semen, fertilization of the egg is not possible through regular intercourse. This often leads to emotional distress and uncertainty for couples trying to start a family. However, the effect of azoospermia and pregnancy is not necessarily permanent or untreatable. Thanks to modern medical advancements, many men diagnosed with this condition can still become biological fathers through assisted reproductive techniques.
When it comes to azoospermia chances of getting pregnant, outcomes depend heavily on the type and severity of the condition. If sperm can be surgically retrieved from the testicles or reproductive tract, techniques like IVF with ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) may offer a viable path to pregnancy. In some cases, donor sperm may also be considered. Early diagnosis and expert consultation at fertility clinics like Vita Altera IVF Center in Cyprus greatly improve the chances of identifying a workable solution and achieving successful conception.
How is Azoospermia Treated?
Treatment options for azoospermia depend on whether the condition is obstructive or non-obstructive. In obstructive cases, surgical procedures may be used to remove the blockage or reconstruct parts of the reproductive system. Some men with blockages caused by vasectomy or injury can undergo microsurgical techniques such as vasovasostomy or epididymovasostomy to restore sperm flow. In other situations, sperm can be directly retrieved from the testicles or epididymis using methods like PESA, MESA, or TESE.
For non-obstructive cases, azoospermia treatment may involve hormonal therapy, lifestyle modifications, or advanced sperm retrieval techniques combined with assisted reproductive technologies. In some instances, no sperm can be found even after retrieval attempts, and the couple may need to consider donor sperm. While not all cases are fully reversible, many men achieve fatherhood through IVF and ICSI once viable sperm is obtained. Thanks to ongoing innovations in male infertility care, an effective azoospermia cure may be possible even in complex scenarios, especially with expert intervention at specialized centers like Vita Altera IVF Clinic.
Azoospermia IVF
For men diagnosed with azoospermia, IVF combined with ICSI offers a powerful solution to achieve biological parenthood. Even in cases where sperm is absent in the ejaculate, surgical retrieval methods can often obtain viable sperm for fertilization. At our Cyprus IVF clinic, we proudly maintain high azoospermia IVF success rates, offering patients renewed hope with every treatment. Our personalized care ensures a strong azoospermia success rate for even the most complex cases.
Micro TESE Procedure
Micro TESE (Microsurgical Testicular Sperm Extraction) is a specialized procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles in men with non-obstructive azoospermia. It is performed under a high-powered microscope to locate areas of sperm production. At Vita Altera, Micro TESE is often combined with IVF treatment in Cyprus, offering couples a strong chance of achieving pregnancy despite severe male infertility.