In the world of assisted reproduction, the term blastocyst holds tremendous importance, especially in the context of in vitro fertilization (IVF). As one of the advanced stages of embryo development, the blastocyst plays a pivotal role in the success of fertility treatments.
But what exactly is a blastocyst, and how does it impact IVF outcomes? In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve into the scientific and practical aspects of blastocysts, their development, implantation, and what to do if a blastocyst transfer doesn’t lead to pregnancy. We’ll also explore the benefits of techniques like frozen blastocyst transfer and address common concerns, such as when to do a pregnancy test after blastocyst transfer. Let’s dive in.
What is a Blastocyst?
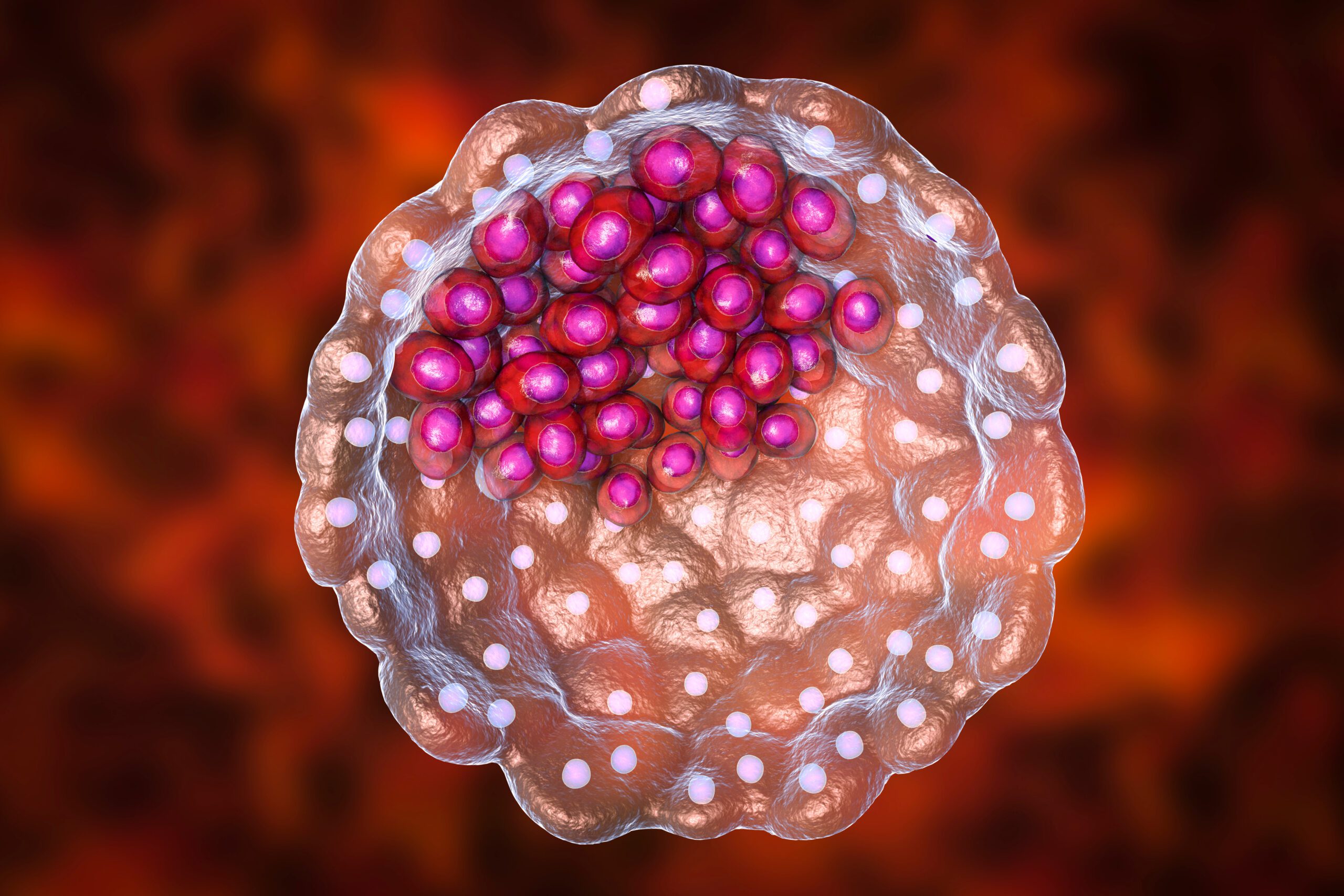
A blastocyst is an advanced stage of an embryo that forms five to six days after fertilization. This is a crucial phase in embryonic development because the blastocyst is biologically prepared to implant into the uterine lining and establish a pregnancy.
Structurally, the blastocyst consists of two key components:
- Inner cell mass (ICM): A group of cells that will eventually develop into the fetus.
- Trophoblast layer: A layer of cells surrounding the blastocyst that forms the placenta, which will support the pregnancy.
So, what is a blastocyst in the context of IVF? In modern IVF practices, embryos are commonly cultured in a lab for five to six days to reach the blastocyst stage before being transferred into the uterus. This technique increases the chances of a successful pregnancy since embryos at this stage are more developed and capable of implantation.
Blastocyst Development and Stages
The development of a blastocyst is a complex but fascinating process. Here’s a breakdown of the stages an embryo goes through before it reaches the blastocyst stage:
- Zygote (Day 1): After fertilization, the single-cell zygote begins dividing into multiple cells.
- Cleavage Stage (Day 2-3): The embryo continues dividing, reaching around 8 cells by Day 3.
- Morula (Day 4): The embryo forms a compact mass of 16-32 cells, resembling a mulberry.
- Blastocyst (Day 5-6): By this stage, the embryo has developed a fluid-filled cavity, along with distinct inner and outer cell structures.
Embryo Grading: How Blastocysts are Assessed
Not all blastocysts are created equal, and embryologists assess their quality using a grading system. This system evaluates the expansion of the blastocyst, the inner cell mass (ICM), and the quality of the trophoblast cells. Examples of embryo grades include:
- 4AA blastocyst: High-quality embryo with well-formed inner and outer cells.
- 3AA blastocysts , 3AB blastocysts and 3BB blastocysts: Viable embryos with slight differences in cell quality.
- 2BB blastocyst: A moderately graded embryo with a lower chance of implantation.
Higher-quality blastocysts are more likely to implant successfully during an IVF cycle.
Blastocysts in IVF
In blastocyst IVF, embryos are cultured in the laboratory until they reach the blastocyst stage, typically on day five or six after fertilization. Culturing embryos to this stage allows embryologists to select the most viable embryos for transfer, increasing the chances of implantation and pregnancy. The advanced techniques employed in IVF, such as embryo grading, help identify high-potential embryos, including 5BC blastocyst and 5 day blastocystWhy Are Blastocysts Used in IVF?
Culturing embryos to the blastocyst stage allows fertility specialists to better assess their potential for successful implantation. Studies show that transferring blastocysts rather than earlier-stage embryos leads to higher pregnancy rates. For example:
- IVF blastocysts are more advanced and biologically capable of implantation.
- A 5 day blastocyst mimics the natural timing of implantation in the uterus, aligning with the body’s natural cycle.
What is a Frozen Blastocyst Transfer?
A frozen blastocyst transfer (FET) involves freezing and storing blastocysts for transfer at a later time. Freezing embryos has become a popular option in IVF as it offers flexibility, reduces physical stress on the patient, and often leads to better implantation rates.
Frozen transfers can be part of a strategy where embryos are preserved until the uterine environment is optimal for implantation.
Frozen Blastocyst Transfer Timeline
The timeline for a 5 day blastocyst frozen embryo transfer typically follows these steps:
- Uterine Preparation: The patient undergoes hormonal treatments (e.g., estrogen and progesterone) to thicken the uterine lining, making it receptive to implantation.
- Thawing the Blastocyst: On the day of transfer, the frozen blastocyst is thawed under strict laboratory conditions.
- Transfer Procedure: The blastocyst is gently placed into the uterus using a catheter, a painless and quick process.
Benefits of Frozen Blastocyst Transfer
There are several advantages to opting for a frozen transfer:
- Higher implantation rates: With more time to recover from the ovarian stimulation phase, the uterine lining becomes more receptive to implantation.
- Reduced risks: Frozen transfers lower the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a condition that can occur after egg retrieval.
- Flexibility: Patients can choose to delay pregnancy to a time that is medically or personally convenient.
When to Do a Pregnancy Test After Blastocyst Transfer?
One of the most common questions among IVF patients is when to do a pregnancy test after blastocyst transfer. Typically, it’s recommended to wait 9-14 days after the transfer for an accurate result. A blood test to measure hCG levels is more reliable than a home pregnancy test during this period.
Symptoms After 5 Day Blastocyst Transfer
Many patients wonder about 5 day blastocyst transfer symptoms. After the transfer, you may experience:
- Mild cramping or bloating.
- Spotting or light bleeding, known as implantation bleeding.
- Breast tenderness or fatigue, similar to early pregnancy symptoms.
Remember, the absence of symptoms doesn’t necessarily indicate a failed transfer, as each person’s body reacts differently.
The 5 day blastocyst transfer success rates tend to be higher compared to earlier-stage embryo transfers. This is due to the more advanced development of the embryo and better synchronization with the uterine environment.
Blastocyst Implantation: What You Need to Know
Blastocyst implantation is the critical step where the blastocyst attaches itself to the uterine lining. The success of implantation depends on several factors:
- The quality of the blastocyst.
- The thickness and receptivity of the uterine lining.
- Hormonal levels and overall health.
The process of blastocyst to implantation marks the beginning of pregnancy and typically occurs within 1-3 days after the transfer.
What Happens if a Blastocyst Doesn’t Implant?
Unfortunately, not all blastocysts lead to successful pregnancies. So, what happens to a blastocyst if it doesn’t implant? In such cases, the embryo is naturally absorbed by the body or expelled during the next menstrual cycle.
Factors Influencing Implantation Success
Several factors can influence the chances of a successful implantation:
- Embryo quality: High-quality embryos, like 4AA blastocysts, have higher implantation rates.
- Uterine receptivity: A uterine lining of at least 8 mm thickness is ideal for implantation.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol, and stress can negatively impact implantation.
Next Steps After a Failed Implantation
If a blastocyst doesn’t implant, there are steps you can take:
- Genetic testing of embryos: This can identify chromosomal abnormalities that may reduce implantation success.
- Optimizing uterine health: Techniques like endometrial scratching or hormonal adjustments may improve the uterine environment.
- Lifestyle modifications: A healthier lifestyle can enhance implantation chances in subsequent cycles.
Your fertility specialist will work with you to develop a personalized plan for your next steps.
The blastocyst represents a critical milestone in embryonic development, particularly in IVF treatments. Culturing embryos to the blastocyst stage allows fertility specialists to select the healthiest and most viable embryos, maximizing the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Techniques like frozen blastocyst transfer provide flexibility and convenience while often yielding higher success rates compared to fresh transfers. Whether you’re navigating the symptoms after a 5 day blastocyst transfer or planning your next steps after a failed implantation, understanding the process empowers you to make informed decisions.
Partnering with reputable clinics like Cyprus IVF Clinic, which offers advanced technologies and personalized care, can make a significant difference in your journey to parenthood. With the right support and knowledge, every step brings you closer to the dream of starting or expanding your family.