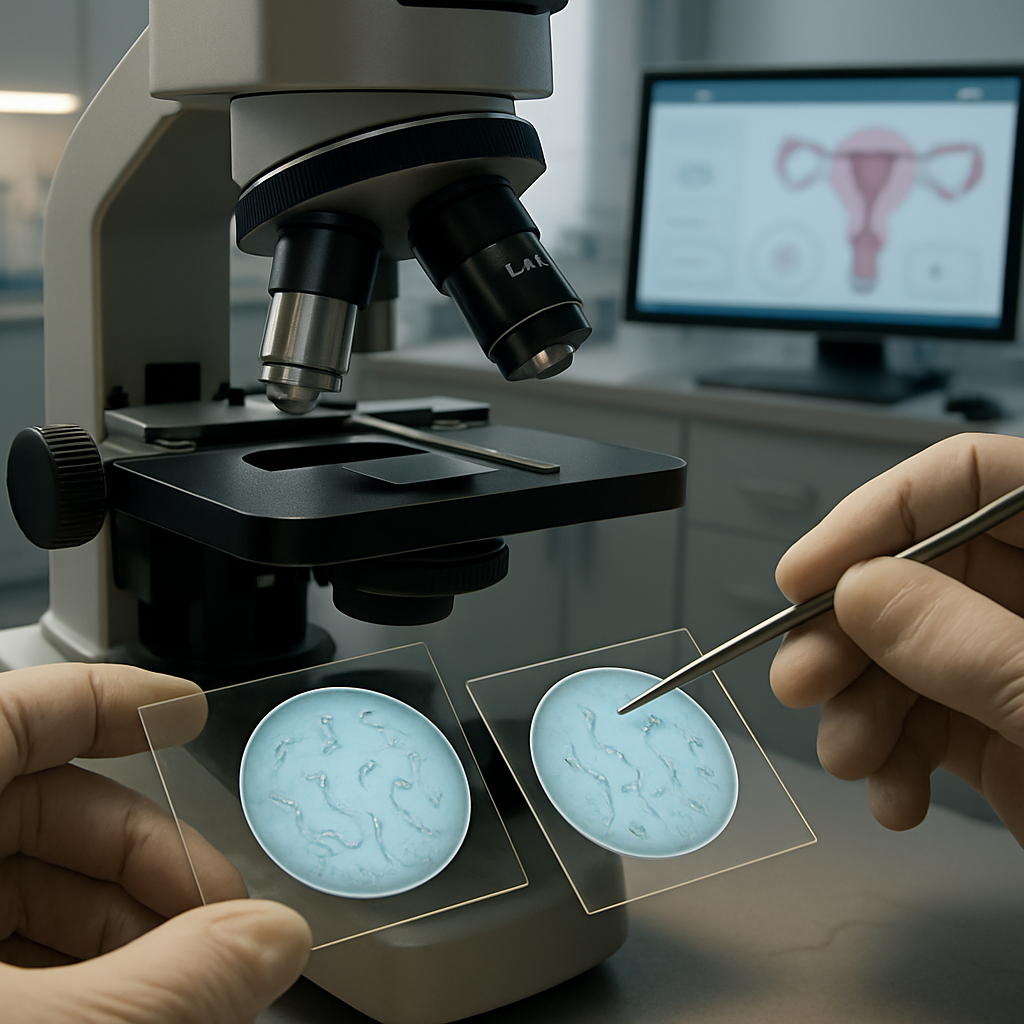
Male Infertility: Symptoms and Treatment
Infertility is a concern that affects countless couples worldwide, with male infertility contributing to approximately 30-50% of cases. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for male infertility is essential for addressing the issue effectively. In this comprehensive blog, we explore the topic in detail, providing insight into diagnosis and treatment options.
What Is Male Infertility?
Male infertility refers to the inability of a man to contribute to conception after 1 year of unprotected sexual intercourse with a fertile partner. This condition often results from problems with sperm production, sperm delivery, or underlying health issues. While challenging, advancements in medical science have made it possible to diagnose and treat many causes of male infertility, offering hope to couples seeking to build a family.
Causes of Male Infertility
The causes of male infertility are varied and often interconnected. Understanding these factors is key to diagnosing and addressing the issue effectively.
Common Causes of Male Infertility
- Low Sperm Count: A reduced number of sperm in the semen can make conception difficult.
- Poor Sperm Motility: Sperm that are unable to swim effectively may struggle to reach and fertilize the egg.
- Abnormal Sperm Morphology: Irregularly shaped sperm may not function properly, reducing their chances of fertilization.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection can hinder successful conception.
Medical Conditions That Cause Male Infertility
Certain medical conditions can directly impact male fertility, including:
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum that affect sperm quality.
- Infections: Conditions like mumps, sexually transmitted infections, or prostatitis can damage reproductive organs.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Issues with testosterone or other hormones critical to sperm production.
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Klinefelter syndrome or Y-chromosome microdeletions can impair fertility.
- Chronic Illnesses: Diabetes and kidney or liver disease can indirectly affect sperm production and sexual function.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Environmental and lifestyle factors play a significant role in male infertility. These include:
- Smoking: Reduces sperm count and motility.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Impacts hormone levels and sperm quality.
- Obesity: Associated with hormonal imbalances and reduced sperm production.
- Exposure to Toxins: Chemicals, heavy metals, and radiation can impair sperm health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect hormone levels and sexual performance.
Signs and Symptoms of Male Infertility
The signs of male infertility are often subtle and may go unnoticed without a medical evaluation. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty conceiving despite regular unprotected intercourse.
- Changes in sexual function, such as reduced libido or erectile dysfunction.
- Pain, swelling, or lumps in the testicular area.
- Abnormal breast growth (gynecomastia), which may indicate hormonal issues.
- Decreased facial or body hair, a potential sign of chromosomal or hormonal abnormalities.
- A low sperm count, which is typically identified through a semen analysis.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance.
 What are the Types of Male Infertility?
What are the Types of Male Infertility?
Male infertility can be classified into different types based on the underlying cause.
Sperm Production Problems
Issues with sperm production are among the most common causes of male infertility. These include:
- Azoospermia: The complete absence of sperm in the semen. This condition can be due to genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, or blockages in the reproductive tract.
- Oligospermia: A low sperm count, where the number of sperm in the semen is below the normal threshold. This can significantly reduce the chances of successful fertilization.
- Teratospermia: High levels of abnormally shaped sperm. These defects in morphology can hinder the sperm’s ability to penetrate the egg.
- Asthenospermia: Poor sperm motility, where sperm struggle to swim efficiently toward the egg. This issue often coincides with other sperm abnormalities.
Structural Abnormalities
Structural problems within the male reproductive system can prevent the proper delivery of sperm. Common issues include:
- Obstructions in the Vas Deferens: These blockages prevent sperm from traveling from the testes to the urethra. They can result from infections, surgeries, or congenital defects.
- Undescended Testicles: A condition where the testicles fail to move into the scrotum during fetal development. This can lead to impaired sperm production and function.
- Retrograde Ejaculation: In this condition, semen flows backward into the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during ejaculation. Retrograde ejaculation may result from diabetes, spinal injuries, or certain medications.
- Hypospadias: A birth defect where the urethral opening is located on the underside of the penis, which can impact the proper release of sperm.
Immunologic Infertility
In rare cases, the immune system may produce antibodies that attack sperm, reducing their ability to fertilize an egg. This condition can result from infections, trauma, or surgeries involving the reproductive organs.
Unexplained Male Infertility
In some cases, the exact cause of male infertility remains unclear despite thorough testing. This type of infertility can be frustrating, but treatments like assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can often help.
Infertility Tests for Male Diagnosis
Diagnosing male infertility involves a series of tests designed to identify the underlying causes.
Basic Tests
- Semen Analysis: The primary test for evaluating sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Hormonal Testing: Measures levels of testosterone, FSH, LH, and prolactin to identify hormonal imbalances.
- Physical Examination: Checks for structural abnormalities, such as varicocele or undescended testicles.
Advanced Diagnostic Methods
- Genetic Testing: Identifies chromosomal abnormalities or genetic conditions affecting fertility.
- Ultrasound: Scans the scrotum and reproductive organs to detect structural issues.
- Testicular Biopsy: Examines testicular tissue to determine sperm production levels.
- Post-Ejaculation Urinalysis: Checks for sperm in the urine to diagnose retrograde ejaculation.
 How is Male Infertility Treated?
How is Male Infertility Treated?
Treatment options for male infertility depend on the underlying cause. Advances in medical science have made it possible to address many forms of infertility successfully.
Medical Treatments
- Hormone Therapy: Used to treat hormonal imbalances by regulating testosterone and other key hormones.
- Medications: Antibiotics for infections, or medications to address erectile dysfunction and other conditions.
Surgical Interventions
- Varicocelectomy: A surgical procedure to repair varicoceles and improve sperm quality.
- Vasectomy Reversal: Reconnects the vas deferens to restore sperm delivery.
- Sperm Retrieval Techniques: Includes procedures like TESE (testicular sperm extraction) for retrieving sperm directly from the testicles.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
ART methods have revolutionized the treatment of male infertility. These include:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Combines sperm and egg outside the body to create embryos for transfer.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): Involves injecting a single sperm into an egg to enhance fertilization chances.
- Cryopreservation: Freezing sperm for use in future fertility treatments.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Fertility
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Helps maintain a healthy weight and reduce stress.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Refrain from smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and recreational drugs.
- Stress Management: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or counseling to manage stress levels effectively.
Final Thoughts
Male infertility is a complex but manageable condition. With advancements in diagnostic tools and treatments, many men can overcome infertility and achieve their dream of fatherhood. Clinics like Cyprus IVF clinic provide cutting-edge solutions tailored to individual needs, offering hope and support to couples worldwide.
If you suspect male infertility, consult a specialist to explore your options and begin your journey toward building a family. By addressing lifestyle factors, seeking timely medical care, and utilizing available technologies, you can take significant steps toward improving fertility outcomes.

 What are the Types of Male Infertility?
What are the Types of Male Infertility? How is Male Infertility Treated?
How is Male Infertility Treated?